Comprehensive Guide to Liabilities to Equity Ratio

If a business chooses to liquidate, all of the company assets are sold and its creditors and shareholders have claims on its assets. Secured creditors have the first priority because their debts were collateralized with assets that can now be sold in order to repay them. This tells you that ABC Widgets has financed 75% of its assets with shareholder equity, meaning that only 25% is funded by debt. This means that for every dollar of equity, Company A has two dollars of debt. This high ratio could indicate a high level of risk, depending on the industry and economic conditions.
- Debt-financed growth may serve to increase earnings, and if the incremental profit increase exceeds the related rise in debt service costs, then shareholders should expect to benefit.
- In most cases, this would be considered a sign of high risk and an incentive to seek bankruptcy protection.
- The Liabilities to Equity Ratio is a financial metric that assesses a company’s financial leverage by comparing its total liabilities to its shareholders’ equity.
- Its D/E ratio would therefore be $1.2 million divided by $800,000, or 1.5.
Sales & Investments Calculators
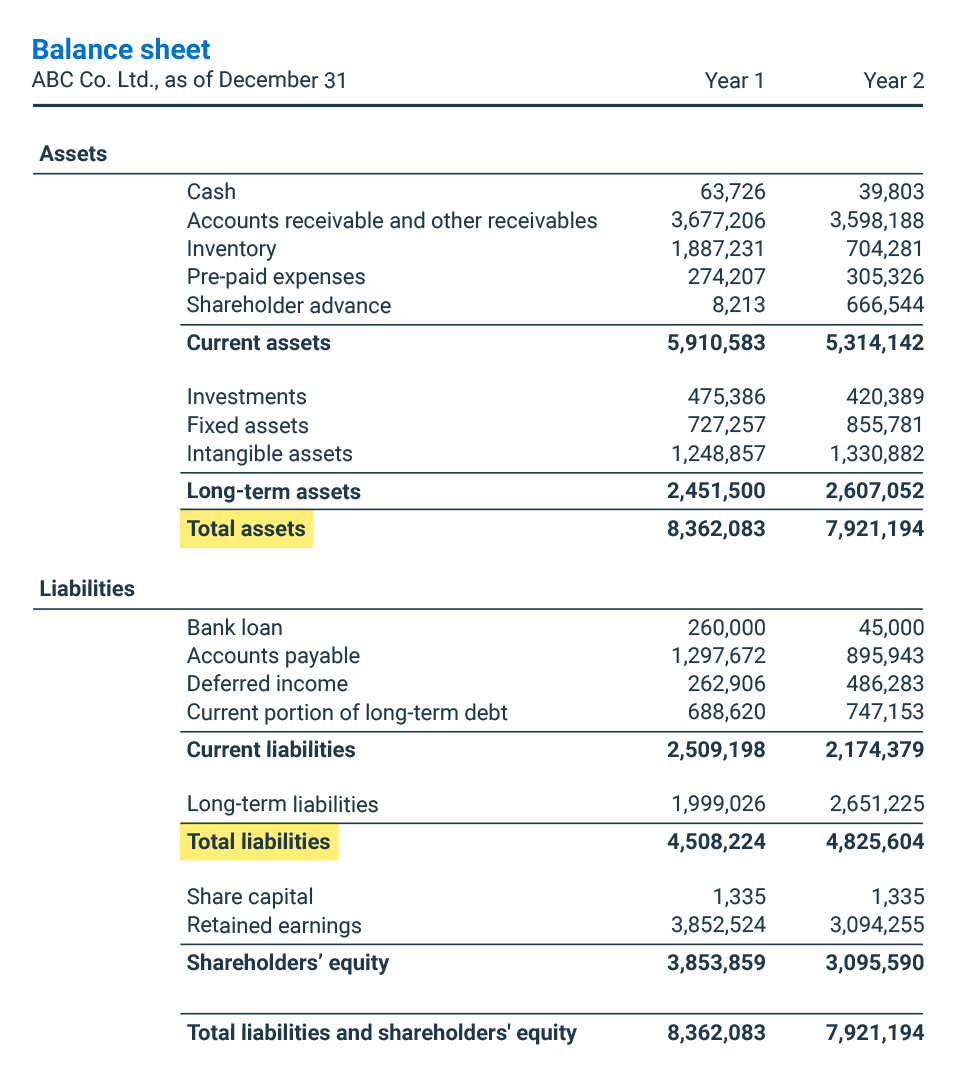
Both ‘Total Liabilities’ and ‘Shareholders’ Equity’ can be found on a company’s balance sheet. Total Liabilities include both current and long-term liabilities, while Shareholders’ Equity refers to the net value of the company, i.e., its assets minus liabilities. In fact, debt can enable the company to grow and generate additional income. But if a company has grown increasingly reliant on debt or inordinately so for its industry, potential investors will want to investigate further. The personal D/E ratio is often used when an individual or a small business is applying for a loan. Lenders use the D/E figure to assess a loan applicant’s ability to continue making loan payments in the event of a temporary loss of income.
Salary & Income Tax Calculators
A higher ratio indicates that a company relies more on debt to finance its operations, which can be riskier, especially during economic downturns. On the other hand, a lower ratio may suggest the company is less risky but may not be taking full advantage of the growth opportunities debt can provide. As a highly regulated industry making large investments typically at a stable rate of return and generating a steady income stream, utilities borrow heavily and relatively cheaply. High leverage ratios in slow-growth industries with stable income represent an efficient use of capital. Companies in the consumer staples sector tend to have high D/E ratios for similar reasons. Liabilities and equity make up the right side of the balance sheet and cover the financial side of the company.
The Formula for the Shareholder Equity Ratio Is
Changes in long-term debt and assets tend to affect the D/E ratio the most because the numbers involved tend to be larger than for short-term debt and short-term assets. If investors want to evaluate a company’s short-term leverage and its ability to meet debt obligations that must be paid over a year or less, they can use other ratios. These balance sheet categories may include items that would not normally be considered debt or equity in the traditional sense of a loan or an asset. Below liabilities on the balance sheet, you’ll find equity, the amount owed to the owners of the company.
Liabilities to Equity Ratio
He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. Understanding the Liabilities to Equity Ratio can offer invaluable insights into a company’s financial health and stability.
Decoding the Intricacies of the Liabilities to Equity Ratio
Everything listed there is an item that the company has control over and can use to run the business. In other words, if ABC Widgets liquidated all of its assets to pay off its debt, the shareholders would retain 75% of the company’s financial resources. Say that you’re considering investing in ABC Widgets, Inc. and want to understand its financial strength and overall debt situation.
Finally, if we assume that the company will not default over the next year, then debt due sooner shouldn’t be a concern. In contrast, a company’s ability to service long-term debt will depend on its long-term business prospects, which are less how should discontinued items be presented on the income statement certain. Business owners use a variety of software to track D/E ratios and other financial metrics. Microsoft Excel provides a balance sheet template that automatically calculates financial ratios such as the D/E ratio and the debt ratio.
Gearing ratios focus more heavily on the concept of leverage than other ratios used in accounting or investment analysis. The underlying principle generally assumes that some leverage is good, but that too much places an organization at risk. To get a clearer picture and facilitate comparisons, analysts and investors will often modify the D/E ratio. They also assess the D/E ratio in the context of short-term leverage ratios, profitability, and growth expectations. The lender of the loan requests you to compute the debt to equity ratio as a part of long-term solvency test of the company. Gearing ratios constitute a broad category of financial ratios, of which the D/E ratio is the best known.
The growing reliance on debt could eventually lead to difficulties in servicing the company’s current loan obligations. Very high D/E ratios may eventually result in a loan default or bankruptcy. A D/E ratio of 1.5 would indicate that the company in question has $1.50 of debt for every $1 of equity.